The lesson is a first dive into the Financial Industry Business Data Model (FIB-DM) content. Our example is the Bank Call Report, a US regulatory requirement, Following the Semantic Compliance® approach, we
- Examine the data requirements
- Use the 15 Fundamental Business Concepts to create a high-level concept map.
- Standardize the concept map based on the FIBO vocabulary for concepts and associations.
- Scope the conceptual data model (CDM) starting with concepts and associations and pulling in supertypes entities
- Review the CDM, comparing to the ontology and discuss next steps to generate a logical data model.
- Excursus: Use the concept Map to scope a FIBO subset
Call Report reference data
For US banks one of the key reports required to be filed is the quarterly Consolidated Report of Condition and Income, generally referred to as the call report or RC report. The Federal Financial Institutions Examination Council (FFIEC) publishes the XBRL taxonomy and bank filings.
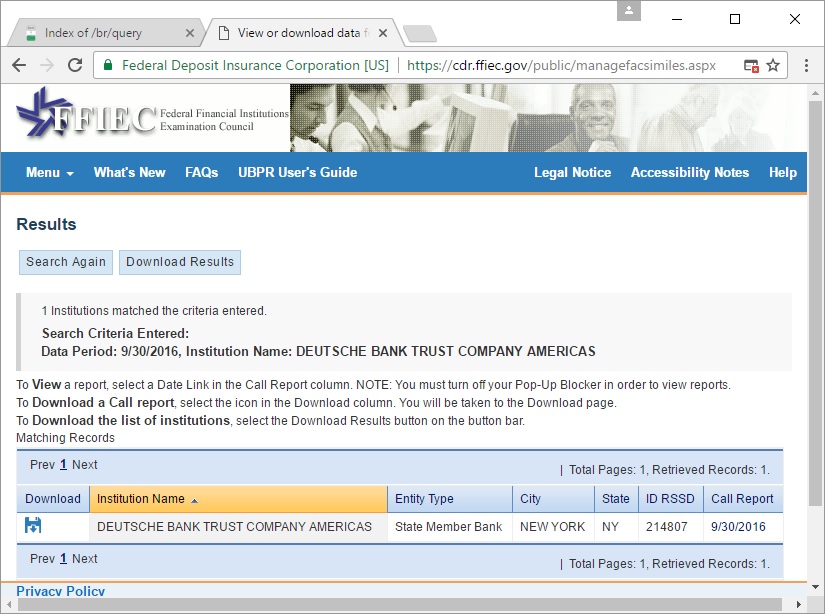
The example below shows JPMorgan Chase Bank, NA submission with call date, id, data item, value, definition, call schedule, and line number.
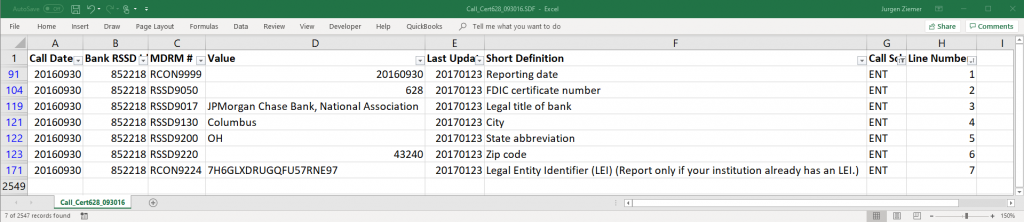
The Entity Schedule, “ENT” has reference data about the reporting Bank. For this exercise, our data requirements are the Entity schedule data items, plus additional reference data about the FFIEC, already in the FIBO.
We draw a simple diagram of our sample data.
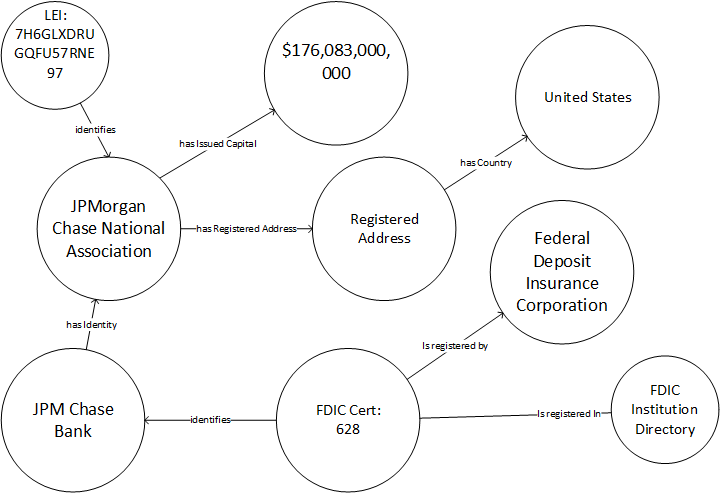
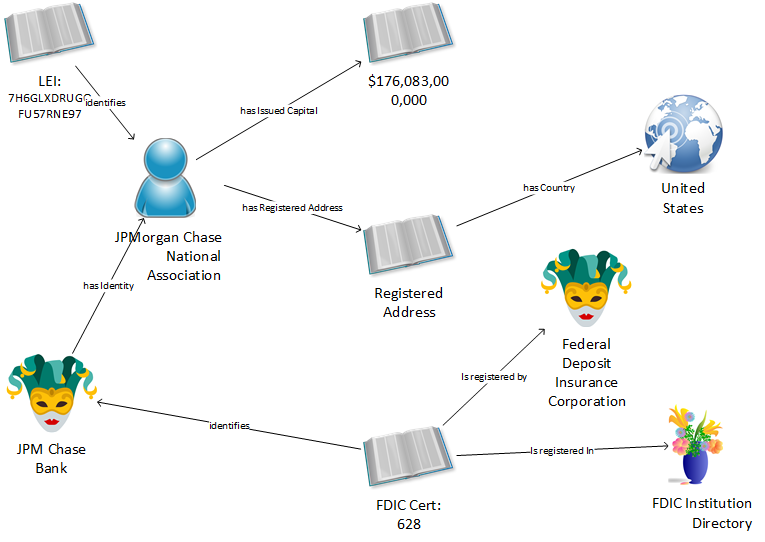
FDIC Certificate 628 identifies JPM Chase as a registered bank. The Certificate is registered in the FDIC Institution Directory. The FDIC registered the Certificate, and thus JPMC. JPMC has the identity of JPMC NA, the legal entity. Note the distinction between what JPMC is—a legal entity—and what JPMC does—taking deposits. The Legal Entity has a registered address with the US as the country. JPMC NA has a Legal Entity Identifier (LEI). The corporation has $176 billion in issued capital.
15 Fundamental Business Concepts
In our second step, we conceptualize our sample data items. That means to assign fundamental business concepts and their specializations.
Here is a picture of the 15 Fundamental Business Concepts.
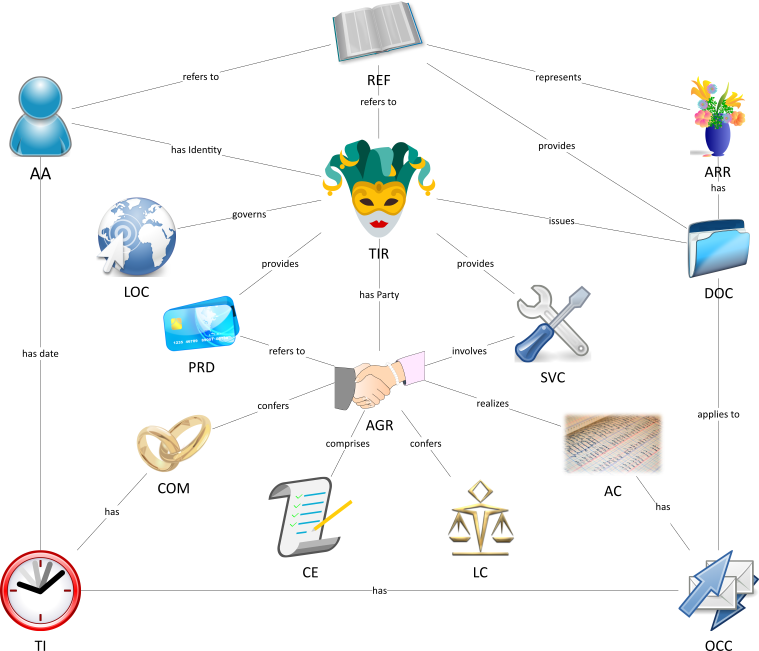
The fifteen concepts are the most extensive ultimate supertypes in the Financial Industry Business Data Model. In other words, they have the most subtypes and relationships. Not counting associative entities, FIB-DM has 1616 base entities. Almost 70% (1101) of base entities are subtypes of the fundamental business concepts. In the FIBO ontology, the fundamental fifteen concepts are direct subclasses of the Thing. We use abbreviations and icons as mnemonics to teach the concepts to modelers and business users.
Creating the concept map diagram
We assign fundamental concepts and their specialization to the data items. The best approach is both top-down, assigning a fundamental concept based on its definition and middle-out, identifying a matching FIB-DM entity. Let’s start with the easy matches:
| FIB-DM has an Entity called Legal Entity Identifier, an exact match for the LEI in the sample. Reference (REF) is the ultimate supertype of Legal Entity Identifier. | ||
| Likewise, we have an Entity named Country in FIB-DM. The country is a specialization of the fundamental concept of Location(LOC). | ||
| The FDIC Certificate Number is another direct match. | ||
| The FDIC Institution Directory is a business Registry. The entity Registry belongs to the Arrangement (ARR) concept. The OMG data model package defines an Arrangement as a structure or means of organizing information such as a schema, numbering system, organization scheme, measurement system, taxonomy, or language for organizing information | ||
| The LEI identifies a Legal Entity. In our example, JPMC NA, a Stock Corporation, an entity in the FIB-DM. The stock corporation is a subtype of the Autonomous Agent (AA). The concept comprises of Person, Legal Person, Automated System, and Organization. | ||
| The FDIC is the Registration Authority that issues the certificate number. The FDIC also has an identity as an Autonomous Agent, but we don’t need that detail for our scope. | ||
| The address fields in our schedule are Registered Addresses, another subtype of Reference. The Reference functions like an associative entity with a role, linking the Country to the Autonomous Agent. | ||
| JPMC’s capital is a Monetary Amount. The entity holds the number and more descriptive properties, such as the currency and date. Following the supertype hierarchy we see that Monetary Amount is a Reference. | ||
| The address fields in our schedule are a Registered Address, another subtype of Reference. The Reference functions like an associative entity with a role, linking Country to the Autonomous Agent. |
We replace the circles in our sample data diagram with shapes of the Fundamental Business Concepts.
Standardize concept map relations
In a similar way, we standardize relationships in our concept map. The data modeler suggests FIB-DM association names that match the related concepts and requirements.
Finally, we replace the sample values with identified FIB-DM entities. Here is our Fundamental Business Concept map for the Call Report Entity Schedule.
I believe the above diagram is easy to understand for non-technical business users. The methodology keeps the concept mapping within the vocabulary and structure of the underlying model.
While this is a small exercise for education purposes, we can see how the diagram expands. The Monetary Amount has more defining concepts; JPMC is a Thing in many more Roles, so is the FDIC; we can add other Regulators to the picture, and so on.
Scoping the Conceptual Data Model
The data modeler transposes the concept map into a data model diagram. In PowerDesigner, we
- create a new diagram and add the identified entities.
- pull in supertypes all the way up to the fundamental concept entity
- we add associations and associative entities
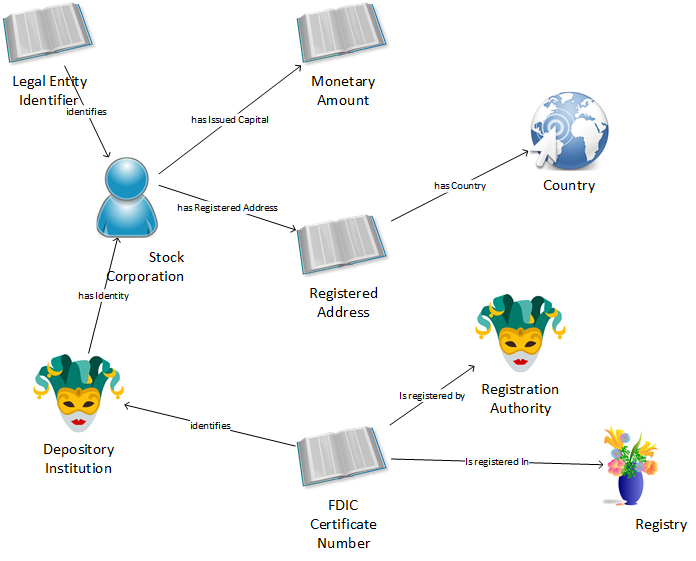
The nine entities from our concept map are marked with green names. The seven relations in the concept map are blue Associations and associative entities in the conceptual data model diagram.
Registration Authority and Depository Institution are subtypes of Service Provider, a Thing in Role. Legal Entity Identifier and FDIC Certificate Number are subtypes of Organization Identifier, a Reference. The Associative Entity is Registered By connecting the FDIC Certificate with the Registration Authority. The Certificate is Registered In a Registry, a Collection subtype of the Arrangement.
The Legal Entity Identifier identifies a Legal Entity, a supertype of our Stock Corporation, or an Autonomous Agent.
The association also identifies the Financial Institution’s legal entity and establishes the many-to-many relationship between the Organization and its Legal Entity.
The Stock Corporation has Issued Capital the Monetary Amount. The Monetary amount is conceptually a measure, subtype of the Reference.
The has Address associative entity connects the Organization to the Physical Address. Note that our more explicit Registered Address and has Registered Address are subtypes of has Address and Physical Address. In other words, the model associates at the supertype level.
The Physical Address has [a] Country, a Geopolitical Entity, subtype of Location.
Discussion – do I really need all these entities?
The short answer is no. Scope only the directly required green entities for a project model.
In practice, the following Logical Modeling phase attributes the model. The Logical Data Modeler looks at the full set of required data items and places them as attributes of the entities. A simple rule:
You can remove any entity in the subtype hierarchy that does not have attributes.
The FIB-DM is a reference data model. For the data modeler, the Financial Industry Business Data Model provides a rich library of building blocks to accelerate the design process. Adhering to the industry standard improves quality and reduces rework. Data and object modelers using the same reference ensures common names, definitions, and design pattern across the organization. Greenfield modeling creates homonyms and synonyms that impede future integration.
Scoping an operational ontology
The 15 Fundamental Business Concepts apply to both the Financial Industry Business Ontology and Data Model. We use the same methodology to create the concept map. With the concept map we can easily scope a subset of the FIBO to hold the regulatory reference data. The Call Report presentation and the Semantic Compliance article on the Bank Ontology website show the instance graph below.
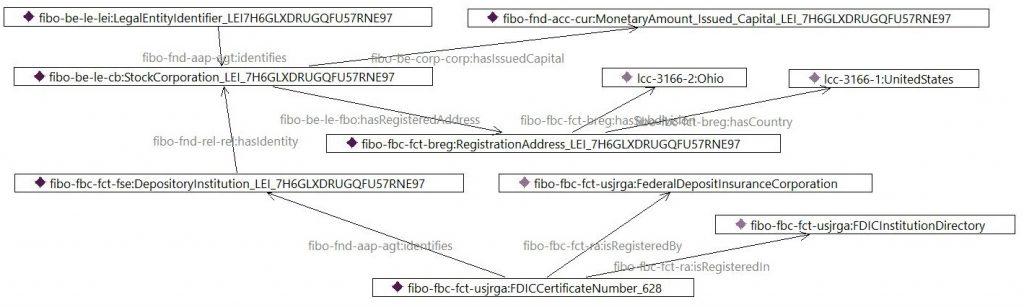
We recognize the very same design pattern as in the sample data concept map.
References
- Financial Industry Business Data Model website: https://fib-dm.com/
- Banking Data Model with diagram gallery and entity definitions: https://bankontology.com/banking-data-model/
- Semantic Compliance, Call Report in FIBO conference presentation: https://bankontology.com/enterprise-data-world-2017-conference-presentation/
- Financial Industry Business Ontology, EDM Council website: https://edmcouncil.org/page/aboutfiboreview